Neural Network
Definition
A single neuron:
x1
x2
. -> a = w' x + b -> y=f(a)
. 1 1xn nx1 1 1
.
x - input
a - activations
w,b - weights and bias, parameters
y - output
f() - activation function
Multi-layers, fully connected
a11 a21 y1
x1 -/> a12 -/> a22 -/> y2
x2 -\> a13 -\> a23 -\> y3
a14 a23 y4
input W1 A1 W2 A2 W3 output
2x1 2x4 4x1 4x4 4x1 4x4 4x1
X -> A1 -> A2 -> Y
W1 W2 W3
+B1 +B2 +B3
A1 = f(W1'X+B1) 4x1
A2 = f(W2'A1+B2) 4x1
Y = f(W3'A2+B3) 4x1
Hyperparameters:
- number of layers
- number of neurons in the layer
- activation function
- number of epoches
Activation Functions
Activation function is a mathematical ‘gate’ in between the input feeding the current neuron and its output going to the next layer
Can be as simple as a step function as switch on and off
Or can be a transformation that maps the input into output
-
step function
a threshold-based activation function
output only 0 or 1f(x) = 1 if x>=0 0 if x<0 -
linear activation function
(+) allow multiple outputs
(-) impossible to use back-propagation, cuz it’s derivative is 1 that has no relation to the input x
(it’s not possible to go back and understand which weights in the input neurons can provide a better prediction)
(-) all layers collapse into one layer, cuz a linear combination of linear cuntions is still a linear functionf(x) = x -
non-linear activation function
(+) allow multiple outputs
(+) allow back-propagation
(+) allow ‘stacking’ of multi layers for deep nn
6 non-linear activation functions
-
sigmoid / logistic
(+) smooth gradient, preventing ‘jumps’ in output
(+) output values bound, between 0 and 1 like normalized
(+) clear predictions, flat in the edges, clear for 0 and 1
(-) vanishing gradient, for very high or very low values of x, there is almost no change to the prediction (flat in the edges) -> slow convergence
(-) outputs not zeros centered, x=0 y=0.5 (-) computationally expensive1 /--- 1 f(x) = ------- / <- 0.5 1+e(-x) 0 ---/ -
tanh / hyperbolic tangent
(+) zero centered, easier to model inputs that have strongly negative, neutral, positive values
(+-) like sigmoide(x)-e(-x) /--- 1 f(x) = ---------- / <- 0 e(x)+e(-x) -1 ---/ -
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU)
(+) computationally efficient, quick convergence
(+) non-linear, allows for back-propagation
(-) the dying ReLU problem, when inputs approach zero or negative, the gradient of the function becomes 0, the network cannot back-propagate and learn/ f(x) = max(0,x) / ----/ <- 0 -
Leaky ReLU
(+) prevents dying ReLU problem
(+-) like ReLU/ f(x) = max(0.1x,x) / __ --/ <- 0 -
softmax
(+) handle multi-class, normalized between 0~1 like probability, sum to 1
(+) useful for output neuronse(x) f(x) = ------ Σ e(x) -
swish
advance ReLUx f(x) = ------- 1+e(-x)
def sigmoid(x):
return 1./(1.+np.exp(-x))
def d_sigmoid(x):
return sigmoid(x)*(1.0-sigmoid(x))
#normalized for numerical stability
def softmax(x):
x=x-x.max()
return np.exp(x)/np.sum(np.exp(x),axis=0)
def relu(x):
return (x>0)*x
def d_relu(x):
return (x>0)*1.0
def linear(x):
return x
def d_linear(x):
return 1.
Loss Function
Regression
-
Mean Square Error (MSE) / L2 Loss / Quadratic Loss
(+) only consider the average magnitude of error irrespective of their direction
(+) square: predictions far away from actual values are penalized heavily
(+) easy gradientJ = 1/N Σ_N (y_i-y_hat_i)^2 -
Mean Absolute Error (MAE) / L1 Loss
(+) like MSE
(-) unlike MSE, needs more complicated tools such as linear programming to compute the gradients
(+) more robust to outliers since it does not make use of squareJ = 1/N Σ_N |y_i-y_hat_i| -
Mean Bias Error
with directionsJ = 1/N Σ_N (y_i-y_hat_i)
Classification
-
multi-class problem
distinguish one item from one pictureoutput target y1 0 class 1 cat y2 1 class 2 dog ✓ y3 0 class 3 rabbit . 0 . . . 0 . . -
multi-label problem
distinguish multiple items from one pictureoutput target y1 1 class 1 cat ✓ y2 0 class 2 dog y3 1 class 3 rabbit ✓ y4 1 class 4 pig ✓ . 0 . -
sigmoid
output: only 0 or 1 -
softmax
output: 0.1,0.2,0.4,… sum up to 1 -
Cross Entropy
CE = - Σ_N y_i * log (y_hat_i) N - #class y_i - groundtruth y_hat_i - network outputs Sigmoid activation + CE Softmax activation + CE -
Binary Classification Problem N=2
CE = - y_1 * log (y_hat_1) - (1 - y_1) * log (1 - y_hat_1) y_1 y_2 = 1 - y_1 y_hat_1 y_hat_2 = 1 - y_hat_1 -
Categorical Cross Entropy Loss / Softmax Loss
softmax activation + CE exp(y_hat_i) f(y_hat)i = ---------------- Σ_N exp(y_hat_j) SoftCE = - Σ_N y_i * log (f(y_hat)i) since y = [0,0,1,0,...] keep only y_i = 1 SoftCE = - log (f(y_hat)i) i <- y_i=1 d SoftCE exp(y_hat_i) --------- = ---------------- - 1 i <- positive class i d y_hat_i Σ_N exp(y_hat_j) d SoftCE exp(y_hat_i) --------- = ---------------- i <- negative class i d y_hat_i Σ_N exp(y_hat_j) -
Binary Cross Entropy Loss / BCE
sigmoid activation + CE 1 f(y_hat_i) = --------------- 1+exp(-y_hat_i) SigCE = - y_1 * log(f(y_hat_1)) - (1 - y_1) * log(1-f(y_hat_1)) /BCE SigCE = - log f(y_hat_i) if y1=1 = - log (1 - f(y_hat_i)) if y1=0 y_1 y_2 = 1 - y_1 y_hat_1 y_hat_2 = 1 - y_hat_2 d SigCE f(y_hat_i) - 1 if y1=1 --------- = D y_hat_i f(y_hat_i) if y1=0 -
Multi Class Loss / Hinge Loss / SVM Loss
J = Σ max (0, s_j - s_y_i + 1) j!=y_i
def d_mse(y_hat,y):
return y_hat-y
def d_bce_sigmoid(y_hat,y):
return y_hat-y
def d_ce_softmax(y_hat,y):
return y_hat-y
Learning process
define the network structure
import nn2
nn=[{'n':784,'act':None}, #input
{'n':10,'act':nn2.relu}, #hidden 1
{'n':10,'act':nn2.softmax,'cost':None}] #output
initialize the weights
def weight_init(nn):
w={}
b={}
for i in range(1,len(nn)):
w[i]=0.001*np.random.rand(nn[i]['n'],nn[i-1]['n'])
b[i]=0.001*np.random.rand(nn[i]['n'],1)
return w,b
- feed-forward
output = W’ * input + B for layers
a1 = f(w1'X+b1) 4x1
a2 = f(w2'a1+b2) 4x1
Y = f(w3'a2+b3) 4x1
def forward(x,w,b,nn):
Z={}
A={}
a=x
A[0]=a
for i in range(1,len(nn)):
z=np.dot(w[i],a)+b[i]
act=nn[i]['act']
a=act(z)
Z[i]=z
A[i]=a
return a,Z,A
- back-propagation without error function
dY/dW, dY/dB, chain rule
z1 = w1'X+b1
a1 = ReLU(z1) 4x1
z2 = w2'a1+b2
a2 = ReLU(z2) 4x1
z3 = w3'a2+b3
Y = ReLU(z3) 4x1
dY dY dz3 dY dY dz3
--- = --- --- --- = --- ---
dw3 dz3 dw3 db3 dz3 db3
0,1 a2 0,1 1
^ ^
δ δ
dY dY dz3 da2 dz2 dY dY dz3 da2 dz2
--- = --- --- --- --- --- = --- --- --- ---
dw2 dz3 da2 dz2 dw2 db2 dz3 da2 dz2 db2
0,1 w3 0,1 a1 0,1 w3 0,1 1
^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^
δ δ
dY dY dz3 da2 dz2 da1 dz1 dY dY dz3 da2 dz2 da1 dz1
--- = --- --- --- --- --- --- --- = --- --- --- --- --- ---
dw1 dz3 da2 dz2 da1 dz1 dw1 db1 dz3 da2 dz2 da1 dz1 db1
0,1 w3 0,1 w2 0,1 x 0,1 w3 0,1 w2 0,1 1
^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^ ^
δ δ
def backward_y(x,w,b,nn):
y_hat,Z,A=forward(x,w,b,nn)
dw={}
db={}
'''
for i in reversed(range(1,len(nn))): #3,2,1
if i==len(nn)-1:
if nn[i]['act'] is relu:
delta=d_relu(y_hat)
else:
delta=np.dot(w[i+1].T,delta)*d_relu(Z[i])
dw[i]=np.dot(delta,A[i-1].T)
db[i]=delta
'''
for i in reversed(range(1,len(nn))): #3,2,1
if nn[i]['act'] is sigmoid:
d_act=d_sigmoid
elif nn[i]['act'] is relu:
d_act=d_relu
elif nn[i]['act'] is linear:
d_act=d_linear
if i==len(nn)-1:
delta=d_act(y_hat)
else:
delta=np.dot(w[i+1].T,delta)*d_act(Z[i])
dw[i]=np.dot(delta,A[i-1].T)
db[i]=delta
return y_hat,dw,db
- back-propagation with error function
def backward_cost(x,y,w,b,nn,cost):
y_hat,Z,A=forward(x,w,b,nn)
dw={}
db={}
for i in reversed(range(1,len(nn))): #3,2,1
if i==len(nn)-1:
if nn[i]['act'] is softmax:
delta=d_ce_softmax(y_hat,y)
elif nn[i]['act'] is sigmoid:
if nn[i]['cost'] is 'BCE':
delta=d_bce_sigmoid(y_hat,y)
if nn[i]['cost'] is 'MSE':
delta=d_mse(y_hat,y)*d_sigmoid(Z[i])
elif nn[i]['act'] is relu:
delta=d_mse(y_hat,y)*d_relu(Z[i])
elif nn[i]['act'] is linear:
delta=d_mse(y_hat,y)*d_linear(Z[i])
else:
if nn[i]['act'] is sigmoid:
d_act=d_sigmoid
elif nn[i]['act'] is relu:
d_act=d_relu
elif nn[i]['act'] is linear:
d_act=d_linear
delta=np.dot(w[i+1].T,delta)*d_act(Z[i])
dw[i]=np.dot(delta,A[i-1].T)
db[i]=delta
return y_hat,dw,db
- calculate loss and accuracy
def accuracy(y_hat,y):
acc=0
for i in range(y_hat.shape[1]):
if y_hat[:,i].argmax()==y[:,i].argmax():
acc+=1
else:
acc+=0
return acc/float(y_hat.shape[1])
def ce_loss(y_hat,y):
loss=-np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat),axis=0,keepdims=True)
return np.mean(loss)
- training
def train(x,y,alpha,iter,w,b,nn,cost=None):
y_hat=np.zeros(y.shape)
acc=np.zeros(iter)
loss=np.zeros(iter)
n=y.shape[1] #data size
for i in range(iter):
for j in np.random.permutation(n):
y_hat,dw,db=backward_cost(x,y,w,b,nn,cost)
for k in range(1,len(nn)):
w[k]=w[k]-alpha*dw[k]
b[k]=b[k]-alpha*db[k]
acc[i]=accuracy(y_hat,y)
loss[i]=ce_loss(y_hat,y)
print('iter:'+str(i+1)+' acc:'+str(acc[i])+' loss:'+str(loss[i]))
return w,b,acc,loss
- testing
def test(x,w,b,nn):
a=x
for i in range(1,len(nn)):
z=np.dot(w[i],a)+b[i] #w[1]*a+b[1] 4x2x2x1+4x1
act=nn[i]['act']
a=act(z)
return a
Mnist Handcoded VS Keras
- test Handcoded
import nn2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from keras.datasets import mnist
import keras
(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test)=mnist.load_data()
#x_train 60000,28,28, y_train 60000,
#x_test 10000,28,28, y_test 10000,
x_train=x_train/255.
x_test=x_test/255.
#one-hot encoding
num_classes=10
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
#take 1000 data samples
x=x_train[:1000,:,:]
y=y_train[:1000]
x_=x_test[:1000,:,:]
y_=y_test[:1000]
x=x.reshape((1000,784))
x=x.T #784x1000
y=y.T #10x1000
x_=x_.reshape((1000,784))
x_=x_.T #784x1000
y_=y_.T #10x1000
nn=[{'n':784,'act':None},
{'n':10,'act':nn2.relu},
{'n':10,'act':nn2.softmax,'cost':None}]
alpha=0.00001
iter=20
(w,b)=nn2.weight_init(nn)
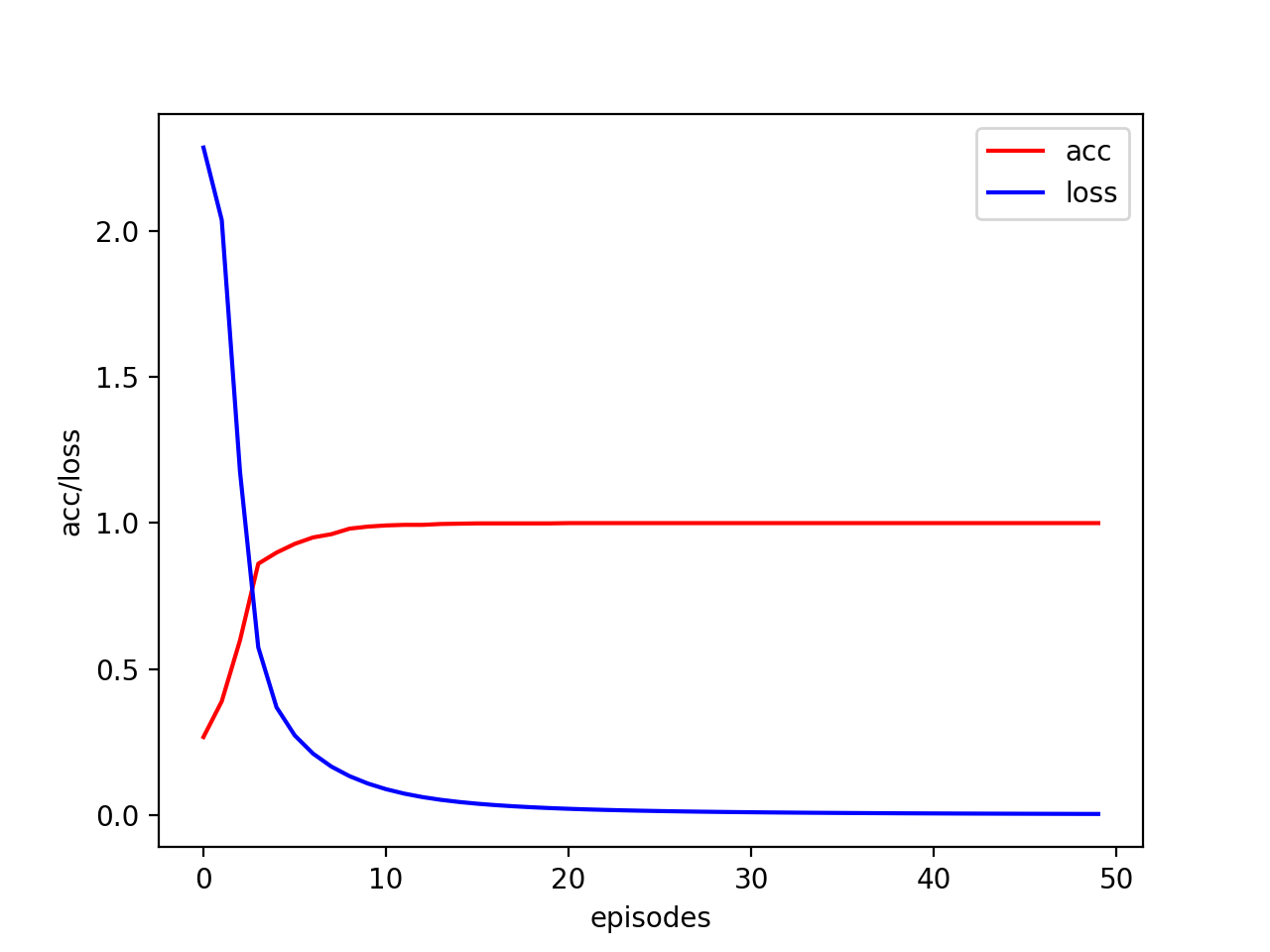
(w,b,acc,loss)=nn2.train(x,y,alpha,iter,w,b,nn)
plt.plot(acc,'r',label='acc')
plt.plot(loss,'b',label='loss')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('episodes')
plt.ylabel('acc/loss')
plt.show()
plt.clf()
plt.jet()
#x_ 784x1000 y_ 10x1000
y_hat=nn2.test(x_,w,b,nn)
import random
#l=random.sample(range(0,1000),8)
l=range(0,8)
for i in range(8):
plt.subplot(2,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(x_[:,l[i]].reshape(28,28))
plt.title('true:'+str(y_hat[:,l[i]].argmax()))
plt.show()

- test Keras
import keras
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import Dense
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.optimizers import SGD
num_classes=10
(x_train,y_train),(x_test,y_test)=mnist.load_data()
#x_train 60000,28,28, y_train 60000,
#x_test 10000,28,28, y_test 10000,
x_train=x_train/255.
x_test=x_test/255.
#one-hot encoding
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, num_classes)
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, num_classes)
x=x_train[:1000,:,:]
y=y_train[:1000]
x_=x_test[:1000,:,:]
y_=y_test[:1000]
x=x.reshape((1000,784))
x_=x_.reshape((1000,784))
alpha=0.1
iter=50
model=Sequential()
#model.add(Dense(10,input_shape=(784,),activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(10,input_dim=784,activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(10,activation='softmax'))
model.summary()
model.compile(optimizer=SGD(lr=alpha),loss='categorical_crossentropy',metrics=['categorical_accuracy'])
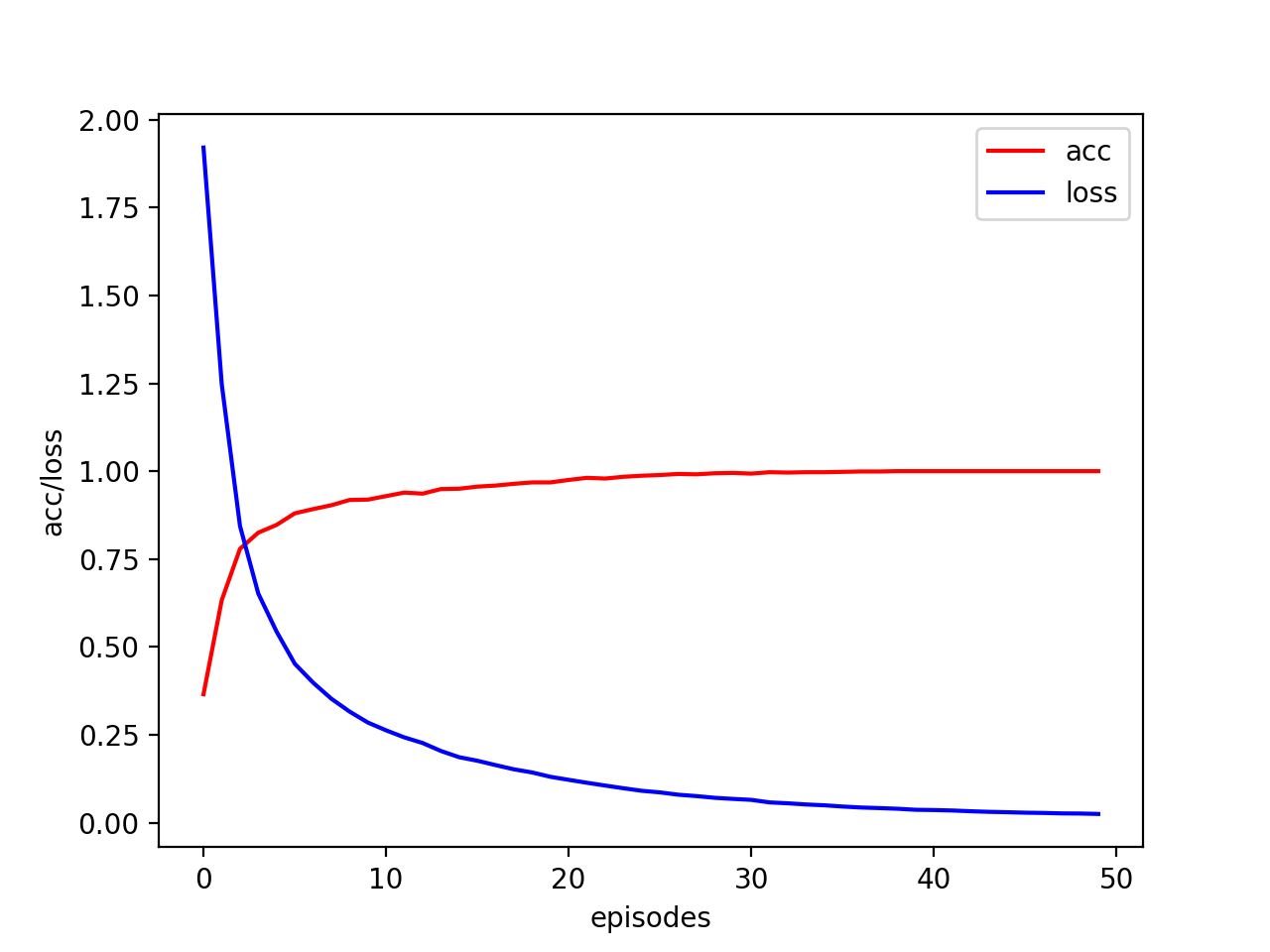
traj=model.fit(x,y,epochs=iter,batch_size=32,shuffle=True)
plt.plot(traj.history['categorical_accuracy'],'r',label='acc')
plt.plot(traj.history['loss'],'b',label='loss')
plt.legend()
plt.xlabel('episodes')
plt.ylabel('acc/loss')
plt.show()
y_hat=model.predict(x_)
import random
#l=random.sample(range(0,1000),8)
l=range(0,8)
for i in range(8):
plt.subplot(2,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(x_[l[i],:].reshape(28,28),cmap='Greys')
plt.title('true:'+str(y_hat[l[i],:].argmax()))
plt.show()

Reference
Code NN in Numpy
an Nth Numpy NN
7 types of activation functions
activation function chart
Understanding Categrotical, Binary Cross Entropy Loss
Loss functions and Derivatives
how to choose loss functions
