ALgorithms 10 - union find
Background
Definition
A disjoint-set data structure is a data structure that keeps track of a set of elements partitioned into a number of disjoint (non-overlapping) subsets.
A union-find algorithm is an algorithm that performs two useful operations on such a data structure:
Find: Determine which subset a particular element is in. This can be used for determining if two elements are in the same subset.
Union: Join two subsets into a single subset.
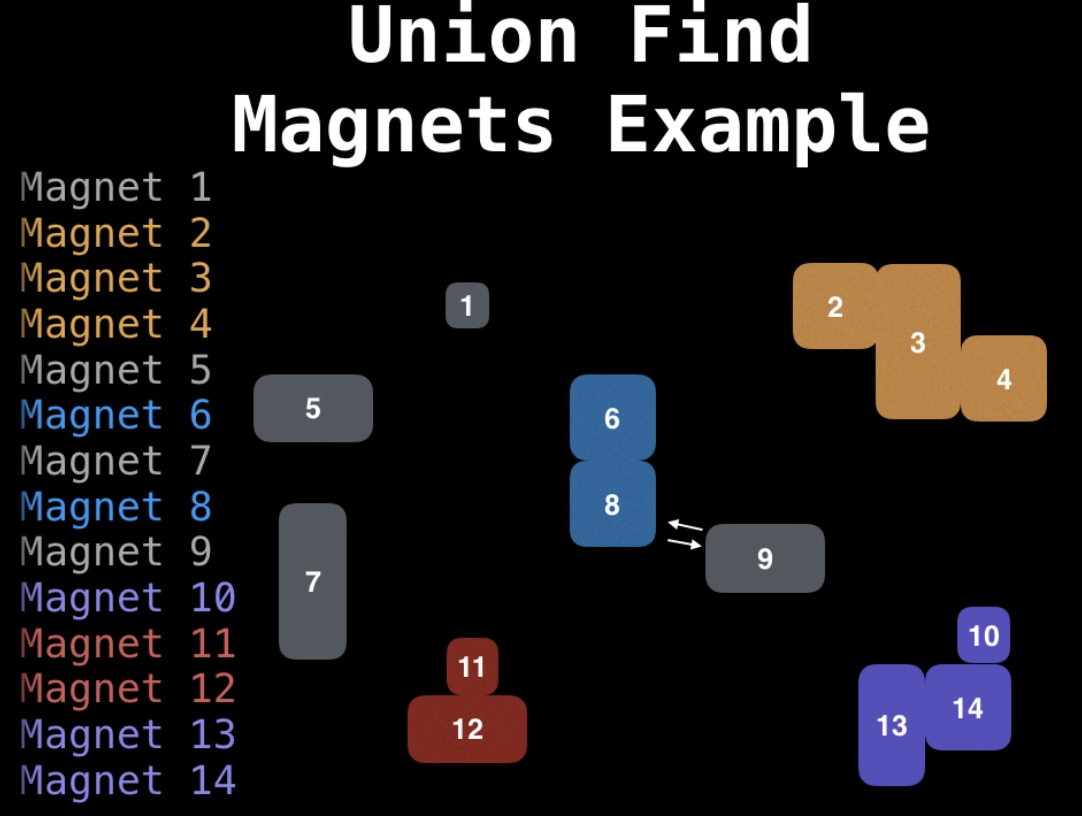
Simple Example:
find closest magnets and merge them into a bigger group
Complexity
O(n) - Construction
A(n) - Union
A(n) - Find
A(n) - Get component size
A(n) - Check if connected
O(1) - Count components
A() - Amortized constant time
Applications
- Kruskal’s minimum spanning tree algorithm
- Grid percolation
- Network connectivity
- Least common ancestor in trees
- Image Processing
Detect Cycle in an Undirected Graph
References: geeks for geeks
Kruskal’s Minimum Spanning Tree
Given a graph G=(V,E) we want to find a minimum spanning tree in the graph (it may not be unique).
A minimum spanning tree is a subset of the edges which connect all vertices in the graph with minimal total edge cost.
Say a graph:
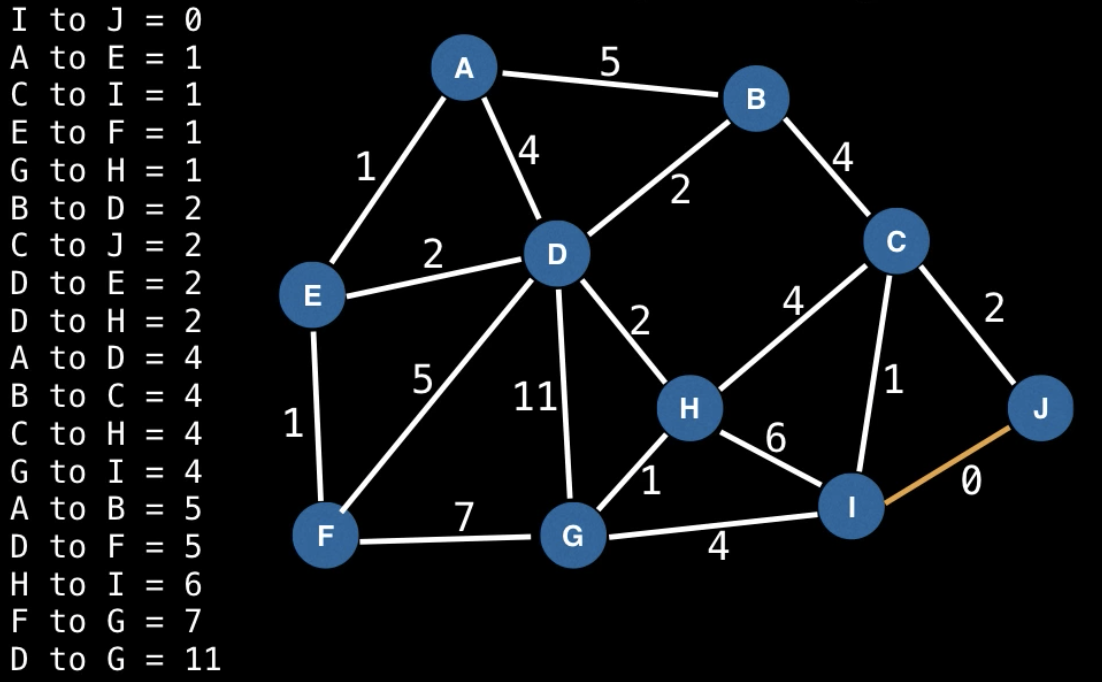
A minimum spanning tree can be
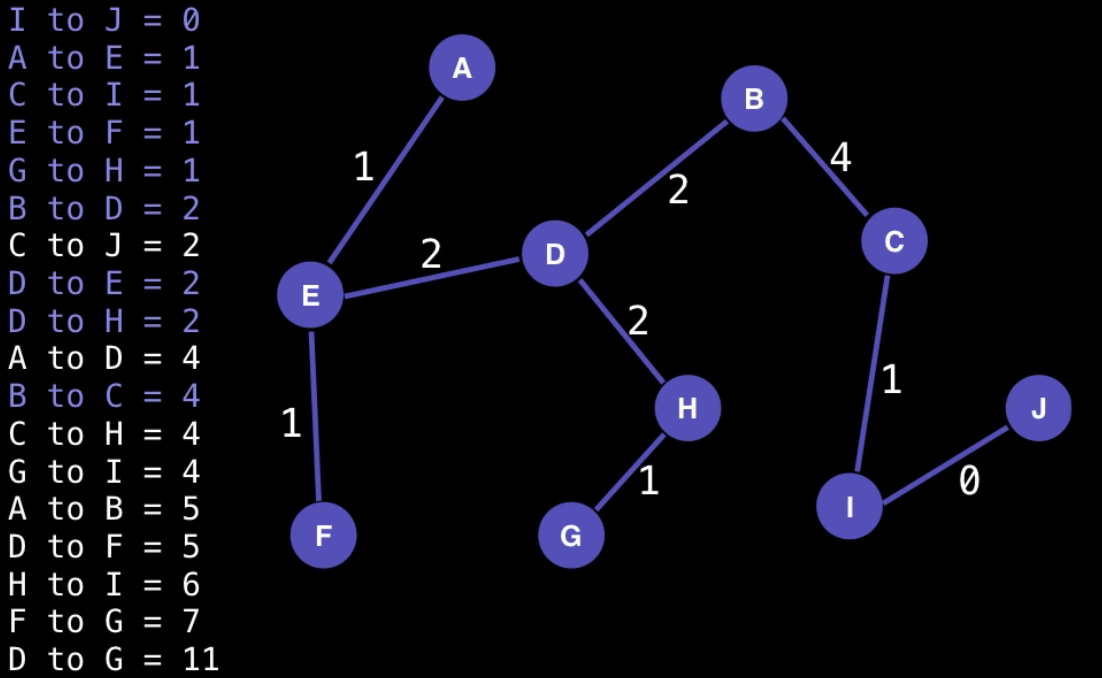
with weight 14
Algorithm steps:
- sort edges by ascending edge weight
- walk through the sorted edges and look at the two nodes the edge belongs to, if the nodes are already unified we don’t include this edge, otherwise we include it and unify the nodes
- the algorithm terminates when every edge has been processed or all the vertices have been unified
Detailed steps based on the example figure above:
- I to J -> I-J
- A to E -> A-E
- C to I -> C-I-J
- E to F -> A-E-F
- G to H -> G-H
- B to D -> B-D
- C to J already in C-I-J would create cycle, do nothing
- D to E -> A-E-F-D-B
- D to H -> A-E-F-D-H-G-B
- A to D already in A-E-F-D-H-G-B would create cycle, do nothing
- B to C -> A-E-F-D-H-G-B-C-I-J minimum spanning tree found!
Implementation from geeks for geeks:
class Graph:
def __init__(self,vertices):
self.V=vertices #No. of vertices
self.graph=[]
#function to add an edge to graph
#w-weight
def addEdge(self,u,v,w):
self.graph.append([u,v,w])
def find(self,parent,i):
if parent[i]==i:
return i
return self.find(parent,parent[i])
def union(self,parent,rank,x,y):
xroot=self.find(parent,x)
yroot=self.find(parent,y)
if rank[xroot]<rank[yroot]:
parent[xroot]=yroot
elif rank[xroot]>rank[yroot]:
parent[yroot]=xroot
else:
parent[yroot]=xroot
rank[xroot]+=1
def KruskalMST(self):
res=[]
i=0 #used for sorted edges
e=0 #used for res
#sort by the weights, which is the third element in self.graph
self.graph=sorted(self.graph,key=lambda item:item[2])
parent=[]
rank=[]
for node in range(self.V):
parent.append(node)
rank.append(0)
while e<self.V-1: #self.V -> numbers of V
u,v,w=self.graph[i]
i+=1
x=self.find(parent,u)
y=self.find(parent,v)
if x!=y:
e+=1
res.append([u,v,w])
self.union(parent,rank,x,y)
return res
g = Graph(10)
g.addEdge(8, 9, 0)
g.addEdge(0, 4, 1)
g.addEdge(2, 8, 1)
g.addEdge(4, 5, 1)
g.addEdge(6, 7, 1)
g.addEdge(1, 3, 2)
g.addEdge(2, 9, 2)
g.addEdge(3, 4, 2)
g.addEdge(3, 7, 2)
g.addEdge(0, 3, 4)
g.addEdge(1, 2, 4)
g.addEdge(2, 7, 4)
g.addEdge(6, 8, 4)
g.addEdge(0, 1, 5)
g.addEdge(3, 5, 5)
g.addEdge(7, 8, 6)
g.addEdge(5, 6, 7)
g.addEdge(3, 6, 11)
print(g.KruskalMST())
>>[[8, 9, 0], [0, 4, 1], [2, 8, 1], [4, 5, 1], [6, 7, 1], [1, 3, 2], [3, 4, 2], [3, 7, 2], [1, 2, 4]]
A-E-F-D-B-C-I-J-H-G
A 0
B 1
C 2
D 3
E 4
F 5
G 6
H 7
I 8
J 9
Problems
leetcode 261 - Graph Valid Tree [M] see graph #problems
Given n nodes labeled from 0 to n-1 and a list of undirected edges, write a function to check whether these edges make up a valid tree.
Input: n=5, edges=[[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,4]]
Output: True
Input: n=5, edges=[[0,1],[1,2],[2,3],[1,3],[1,4]]
Output: False
References:
WilliamFiset fr Youtube
geeks for geeks
